Trump flushes woke programs at Smithsonian museums, orders return of leftist-targeted statues

The left's long march through the institutions was a resounding success. Numerous businesses, churches, libraries, law enforcement agencies, schools, and other organizations have for decades served as incubators for radical activists and amplifiers for pernicious ideologies.
Leftist marchers are, however, now being routed.
Conservatives and other normalcy advocates have in recent years undertaken a reconquest, enjoying success with certain academic institutions such as the New College of Florida as well as major businesses including Walmart, Harley-Davidson, and John Deere.
President Donald Trump — who has taken an axe to DEI, critical race theory, and gender ideology in the federal government and in federally funded organizations — continued his D.C.-focused purge of radicalism on Thursday, this time taking aim at the nation's premier museums.
Trump intends to rid the Smithsonian Institution, its 21 museums and 14 education and research centers, and the National Zoo of radical leftist programs, policies, and installations.
In an executive order titled "Restoring Truth and Sanity to American History," the president noted, "Over the past decade, Americans have witnessed a concerted and widespread effort to rewrite our Nation's history, replacing objective facts with a distorted narrative driven by ideology rather than truth."
'Museums in our Nation's capital should be places where individuals go to learn — not to be subjected to ideological indoctrination.'
"This revisionist movement seeks to undermine the remarkable achievements of the United States by casting its founding principles and historical milestones in a negative light," continued Trump. "Under this historical revision, our Nation's unparalleled legacy of advancing liberty, individual rights, and human happiness is reconstructed as inherently racist, sexist, oppressive, or otherwise irredeemably flawed."
Trump slammed the Biden administration for advancing this "corrosive ideology" and cited the following as examples of the anti-American propaganda at issue.
- The Smithsonian American Art Museum's exhibit "The Shape of Power: Stories of Race and American Sculpture," which represents that "[s]ocieties including the United States have used race to establish and maintain systems of power, privilege, and disenfranchisement."
- The National Museum of African American History and Culture's assertions that the nuclear family, rugged individualism, self-reliance, prioritization of work over play, emphasis on rational linear thinking, punctuality, decisiveness, and a future-oriented outlook are "aspects and assumptions of whiteness and white culture in the United States."
- The "forthcoming Smithsonian American Women's History Museum plans on celebrating the exploits of male athletes participating in women's sports."
The Smithsonian also enraged conservatives in recent years with the National Museum of American History's Hispanic exhibit portraying religion and history through a Marxist lens and the Smithsonian Institution's 2020 "Girlhood" exhibit featuring the racist founder of Planned Parenthood, Margaret Sanger, and a medical transvestite.
Trump directed Vice President JD Vance to work with senior staffers to "remove improper ideology" from the Smithsonian Institution and its museums, education and research centers, and the National Zoo.
Trump also tasked Vance and Russell Vought, director of the Office of Management and Budget, to work with congressional lawmakers to ensure that Congress avoids bankrolling exhibits or programs at the Smithsonian Institution that "degrade shared American values, divide Americans based on race, or promote programs or ideologies inconsistent with Federal law and policy."
Cognizant and critical of the Smithsonian American Women's History Museum's initiative to feature male cross-dressers in future exhibits, Trump also insisted that the museum does "not recognize men as women in any respect."
"Museums in our Nation's capital should be places where individuals go to learn — not to be subjected to ideological indoctrination or divisive narratives that distort our shared history," said Trump's order.
In addition to flushing leftist radicalism out of the Smithsonian museums, Trump — whose administration has been reverting the names of federal lands and military bases to what they were before Joe Biden took office — set his sights on a restoration of that which the iconoclasts of yesteryear chose to eliminate from the public consciousness.
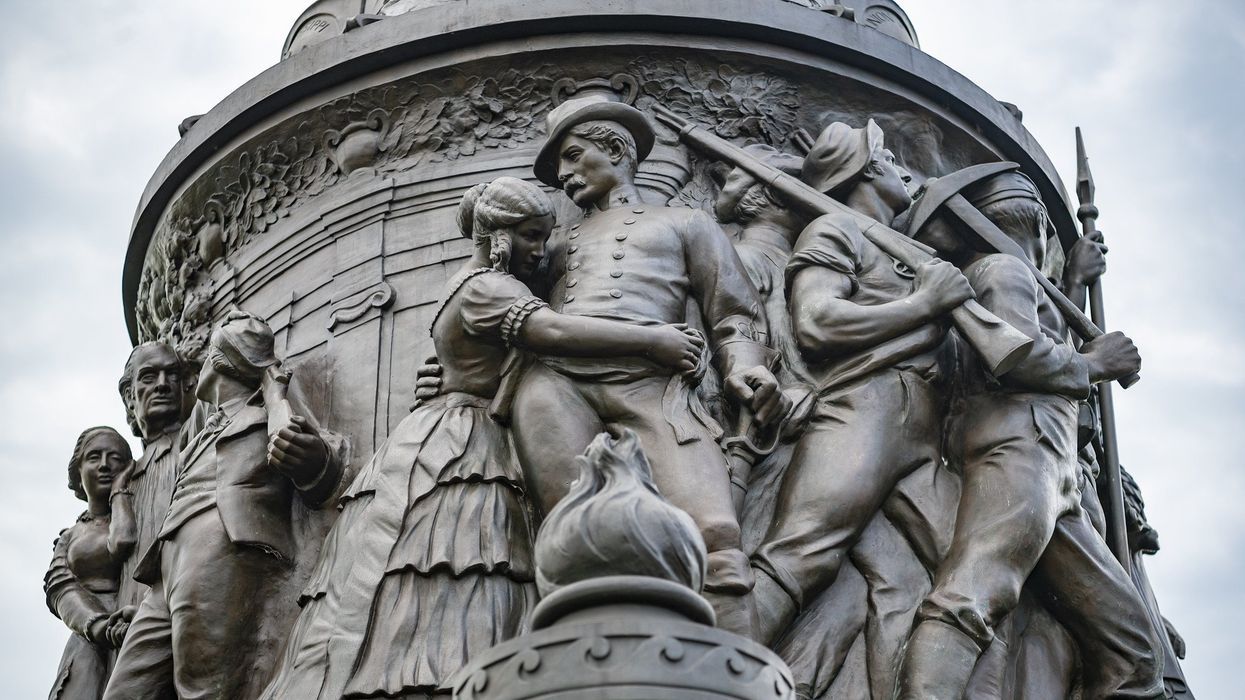
Radicals both inside and outside government committed to a campaign of destruction and deracination in the wake of George Floyd's death in 2020, digging up graves, toppling statues, renaming animals, melting down busts, and knocking out church windows.
Trump directed Secretary of the Interior Doug Burgum to figure out whether public monuments, memorials, statues, or other properties within the Interior Department's jurisdiction were removed or changed during this radical campaign "to perpetuate a false reconstruction of American history, inappropriately minimize the value of certain historical events or figures, or include any other improper partisan ideology."
The president demanded further the reinstatement of pre-existing monuments that were removed.
Like Blaze News? Bypass the censors, sign up for our newsletters, and get stories like this direct to your inbox. Sign up here!
 Only in America are anti-American activists given such liberty to express their disdain for everything our nation represents.
Only in America are anti-American activists given such liberty to express their disdain for everything our nation represents.