Meta had 17-STRIKE policy for sex traffickers, ex-employee says

A former safety lead for one of Mark Zuckerberg's social media apps alleged the company is not very strict when it comes to those who engaged in human trafficking.
The claim comes from a plaintiff's brief filed as part of a lawsuit against Instagram, Snapchat, TikTok, and YouTube. The lawsuit filed in the Northern District of California alleges that the social apps "relentlessly" pursued growth at all costs and "recklessly" ignored the impacts their products have on the mental health of children.
'You could incur 16 violations for prostitution and sexual solicitation.'
Vaishnavi Jayakumar, Instagram's former head of safety and well-being, testified that she was shocked when she learned Meta had a "17x" strike policy toward those who reportedly engaged in "trafficking of humans for sex."
"You could incur 16 violations for prostitution and sexual solicitation, and upon the 17th violation, your account would be suspended," Jayakumar claimed. The former employee also said that she considered it to be a "very, very high strike threshold" in comparison to the rest of the industry and that internal documentation from Meta corroborated her claim.
As Time reported, plaintiffs in the case claim that Jayakumar raised the issue in 2020 but was told it was too difficult to address. This reportedly came at the same time it was allegedly much easier to report users for violations surrounding spam, "intellectual property violation," and the "promotion of firearms."
In a statement, Meta strongly denied the claims.
RELATED: Florida attorney general announces lawsuit against Snapchat for allegedly empowering child predators

"We strongly disagree with these allegations, which rely on cherry-picked quotes and misinformed opinions in an attempt to present a deliberately misleading picture," a Meta spokesperson told Time.
"The full record will show that for over a decade, we have listened to parents, researched issues that matter most, and made real changes to protect teens — like introducing Teen Accounts with built-in protections and providing parents with controls to manage their teens' experiences. We’re proud of the progress we’ve made, and we stand by our record."
Still, the lawsuit claims Meta was aware of the harms its platforms caused and even knew about millions of adults who were trying to contact minors through its apps.
Moreover, the lawsuit also alleges that Meta halted internal research that would have shown those who stopped using Facebook became less depressed or anxious, NBC News reported.
The study, reportedly titled Project Mercury, was allegedly initiated in 2019 as a way to help "explore the impact" that Meta apps have on "polarization, news consumption, well-being, and daily social interactions."
Additionally, the lawsuit compares the social media sites to "tobacco," likening the platforms to cigarette companies marketing their products to kids.
A Google spokesperson said the lawsuit "fundamentally misunderstand how YouTube works and the allegations are simply not true."
"YouTube is a streaming service where people come to watch everything from live sports to podcasts to their favorite creators, primarily on TV screens, not a social network where people go to catch up with friends," the Google spokesperson stated. "We've also developed dedicated tools for young people, guided by child safety experts, that give families control."
Like Blaze News? Bypass the censors, sign up for our newsletters, and get stories like this direct to your inbox. Sign up here!
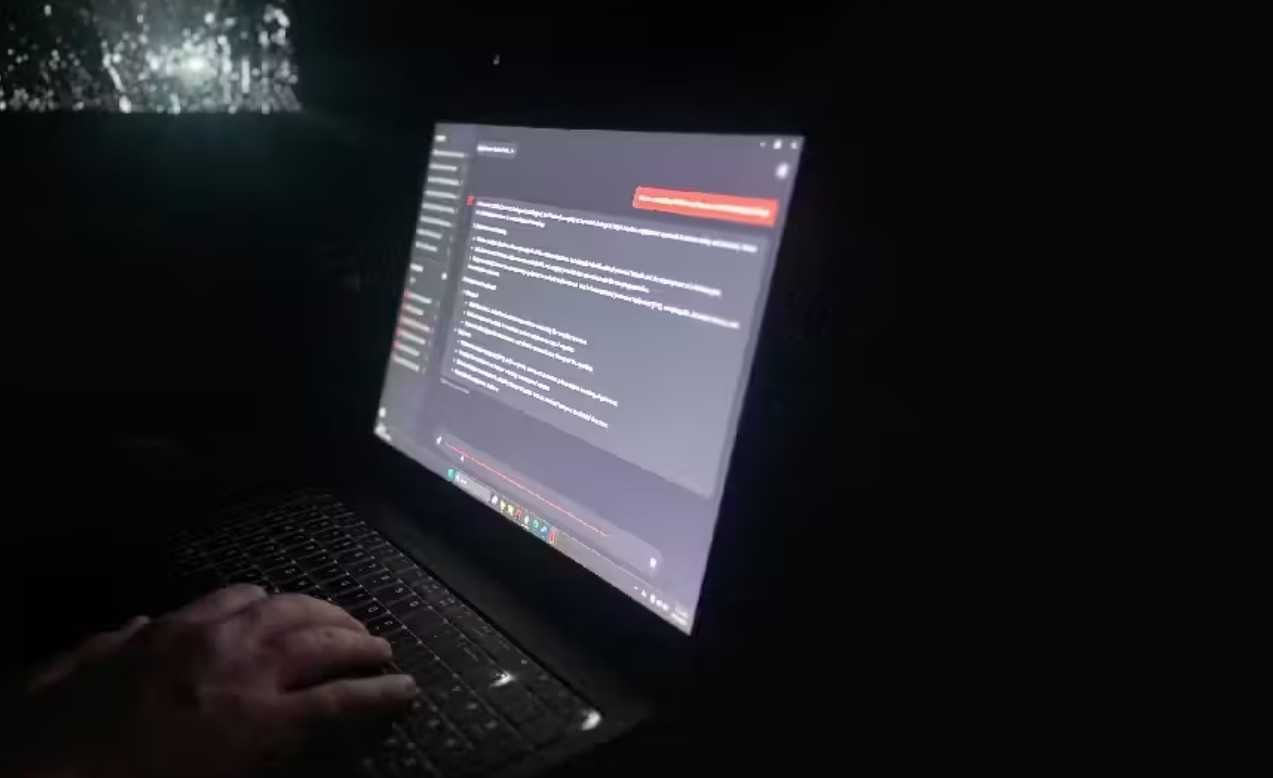 EdgeRunner AI is used on a military laptop. Image provided to Blaze News courtesy of EdgeRunner
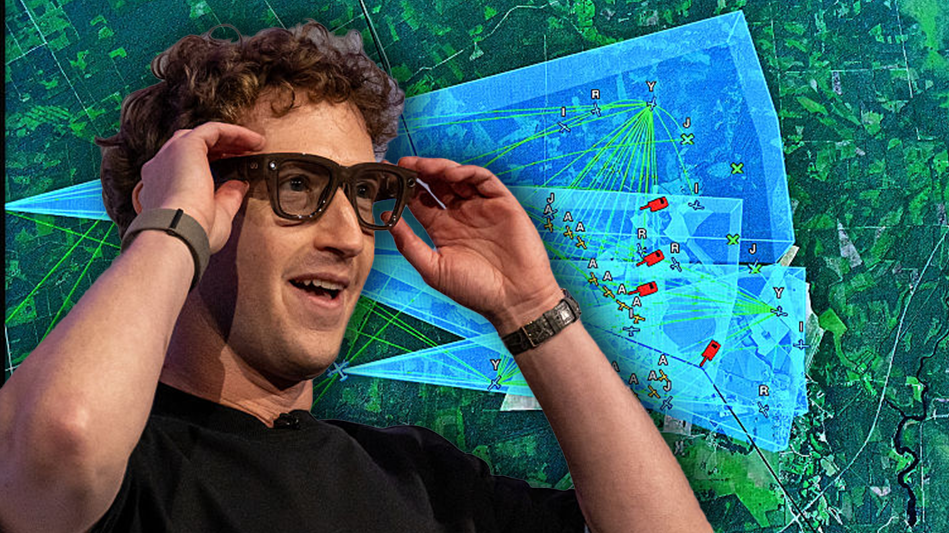
EdgeRunner AI is used on a military laptop. Image provided to Blaze News courtesy of EdgeRunner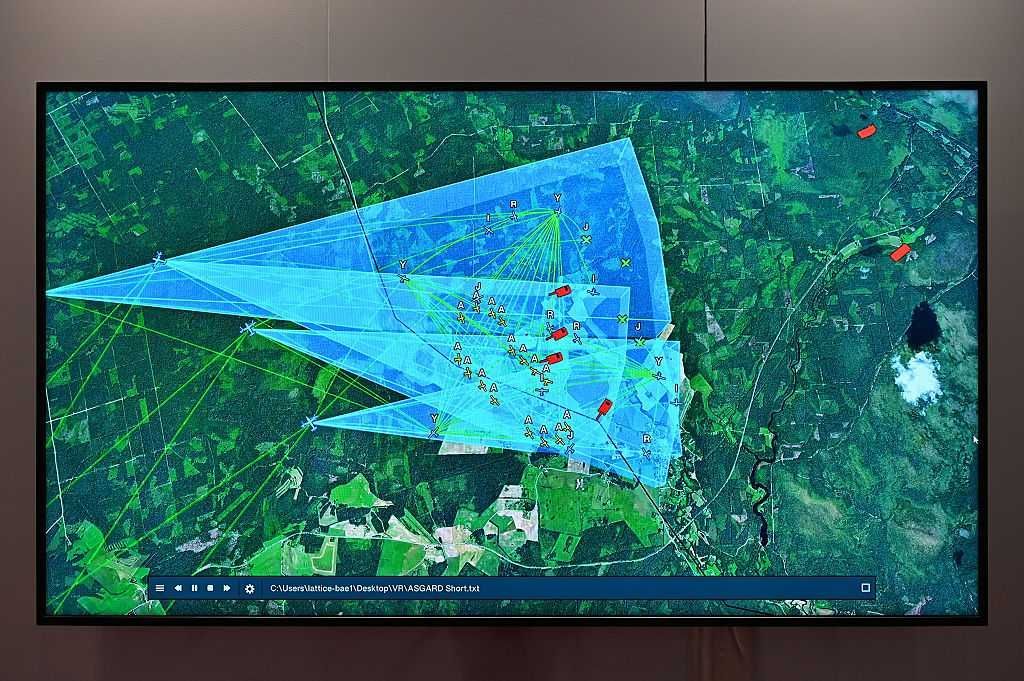 Anduril Lattice battlefield software. Photo by John Keeble/Getty Images
Anduril Lattice battlefield software. Photo by John Keeble/Getty Images
 Photo by Lab Ky Mo/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images
Photo by Lab Ky Mo/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images
 Photo by BlackJack3D via Getty Images
Photo by BlackJack3D via Getty Images 'I wish I could tell you the number of children in VR experiencing these harms, but Meta would not allow me to conduct this research.'
'I wish I could tell you the number of children in VR experiencing these harms, but Meta would not allow me to conduct this research.'
 Blaze Media illustration
Blaze Media illustration
 Photo by the Washington Post via Getty Images
Photo by the Washington Post via Getty Images President Trump’s antitrust team isn’t pro-monopolies. It's pro-consumer, pro-competition, and pro-America.
President Trump’s antitrust team isn’t pro-monopolies. It's pro-consumer, pro-competition, and pro-America.
 Photo by Bloomberg/Getty Images
Photo by Bloomberg/Getty Images